In various industrial applications, cameras play a pivotal role in capturing critical data, facilitating quality control, and ensuring operational efficiency. Understanding the different types of cameras used in these industries is essential for making informed decisions regarding the most suitable technology for specific applications. This article explores three prominent camera types used in the industry: Area Scan, Rolling Shutter, and Global Shutter.
Area Scan Cameras:
Area Scan cameras, also known as 2D cameras or frame-based cameras, are commonly used in industrial imaging applications. These cameras capture images by scanning the entire field of view one pixel row at a time. The image sensor of an area scan camera is divided into an array of pixels, and each pixel records the light intensity it receives. Once the entire array is scanned, a complete 2D image is obtained. Area scan cameras are further divided into two subtypes based on their shutter mechanisms: Rolling Shutter and Global Shutter.

Rolling Shutter Cameras:
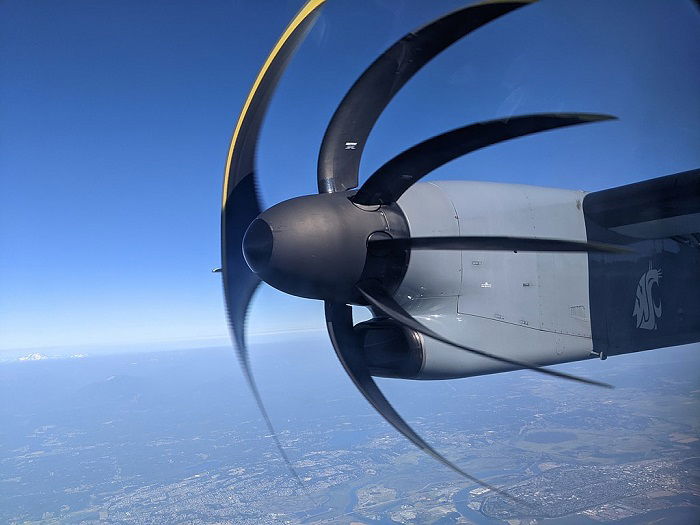
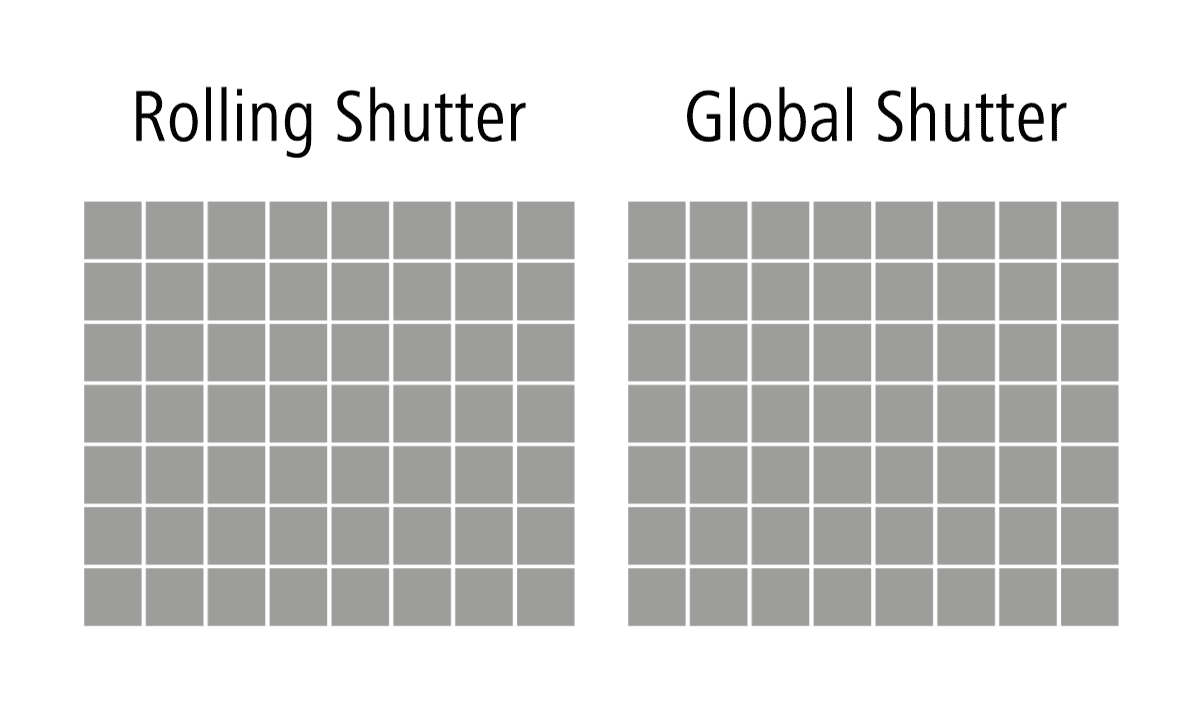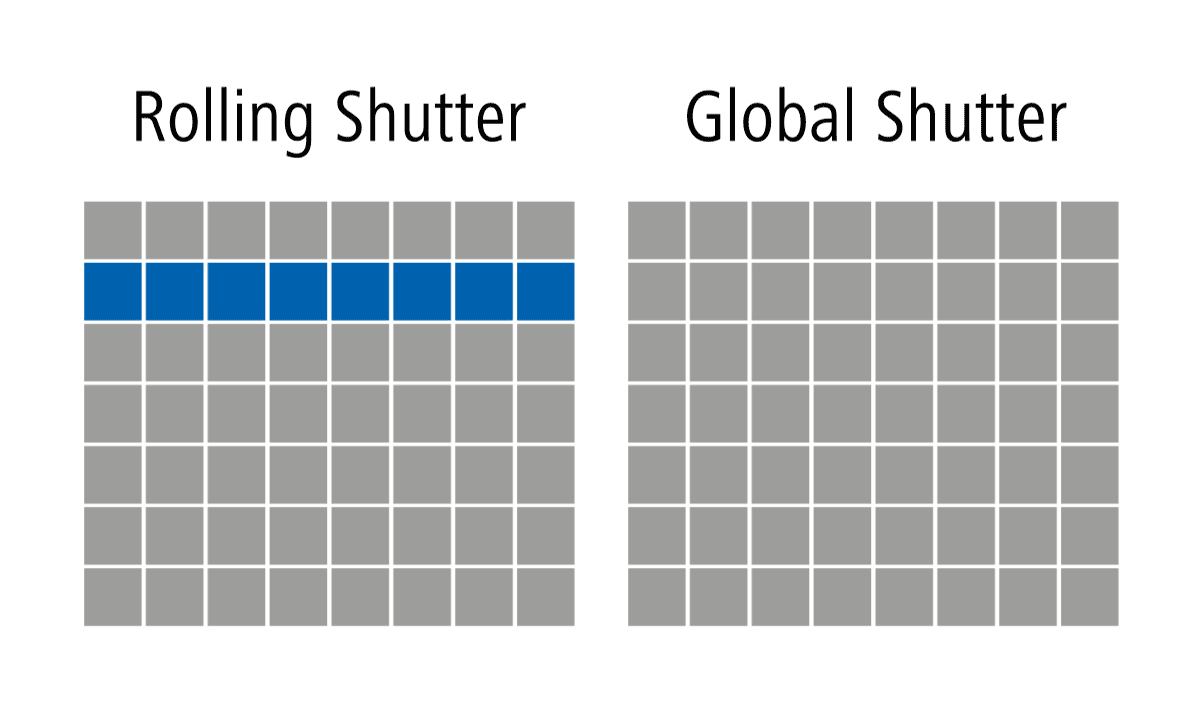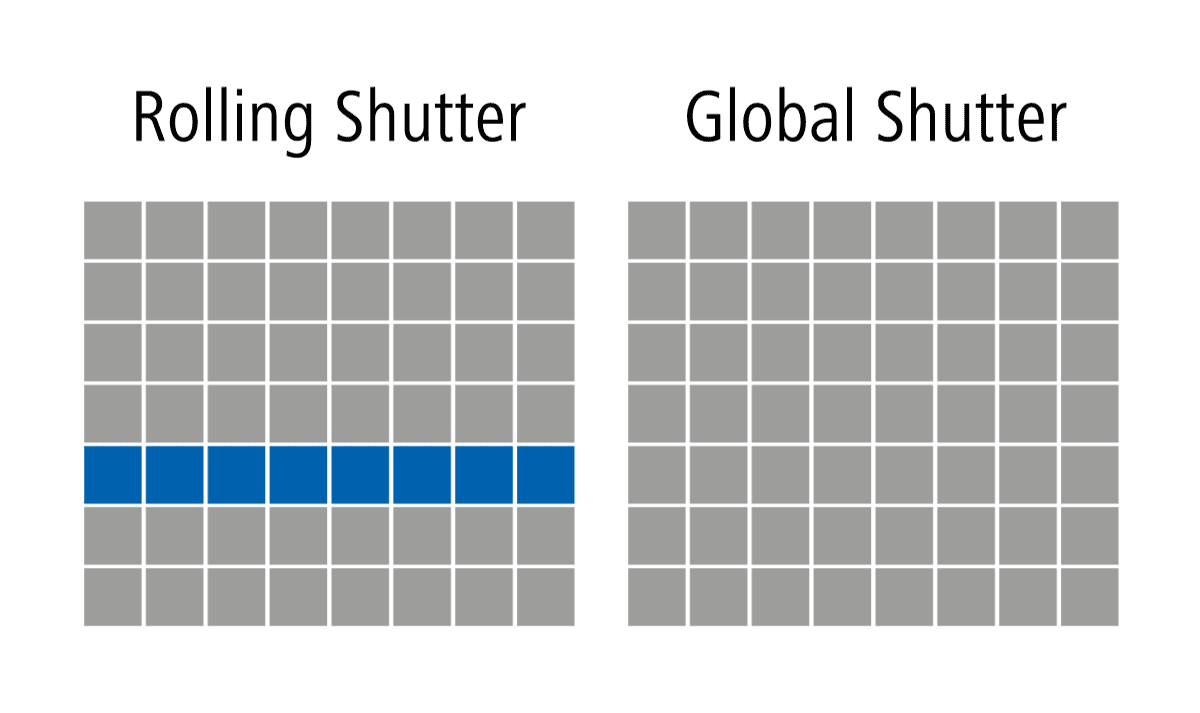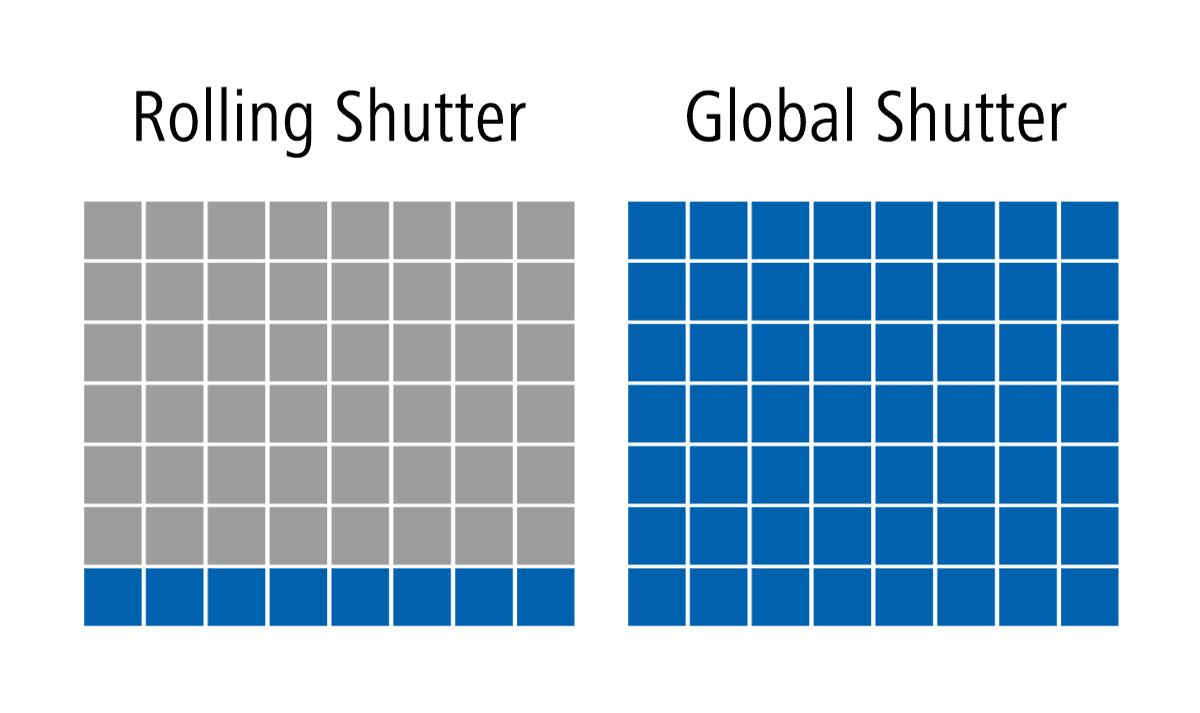
Rolling Shutter cameras are a prevalent type of area scan cameras utilized in the industry. In a rolling shutter mechanism, the camera’s image sensor scans and captures the image row by row, from the top to the bottom of the frame. This sequential scanning can introduce distortions in the image, especially when capturing fast-moving objects or in scenes with rapid motion. The rolling shutter effect can cause image artifacts, such as skewing or the appearance of « jello » effects. However, these cameras are often cost-effective and suitable for applications where motion artifacts are not critical.

Global Shutter Cameras:
Global Shutter cameras are another type of area scan cameras, offering distinct advantages over their rolling shutter counterparts. In a global shutter mechanism, all the pixels in the image sensor are exposed simultaneously, capturing the entire image at once. This eliminates the rolling shutter artifacts and ensures that all parts of the image are captured simultaneously, making them ideal for applications with fast-moving objects or scenes with rapid motion changes. Global shutter cameras are commonly used in high-speed imaging, robotics, inspection systems, and other critical applications where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Comparison between Rolling Shutter and Global Shutter Cameras:
- Rolling Shutter cameras are generally more affordable compared to Global Shutter cameras.
- Global Shutter cameras provide superior image quality, especially in scenarios with fast motion, by eliminating rolling shutter artifacts.
- Rolling Shutter cameras may suffice for static scenes or applications with minimal motion, where cost is a significant consideration.
Conclusion:
In summary, understanding the different types of cameras used in industrial applications is essential for choosing the most appropriate technology for specific use cases. Area Scan cameras, with their subtypes of Rolling Shutter and Global Shutter, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. While Rolling Shutter cameras are more budget-friendly, Global Shutter cameras provide superior image quality and are better suited for applications with fast motion. Careful consideration of the application requirements and budget constraints will aid in making the best choice to achieve optimal results in various industrial settings.
